1N4007 V.S. 1N5408
What can the 1N4007 diode be replaced with? What is the difference between 1n5408 and 1n4007? These two questions are often asked by electronic engineers and hobbyists. This article answers these questions and provides more information about them.

The 1N5408 and 1N4007 differ in the following ways: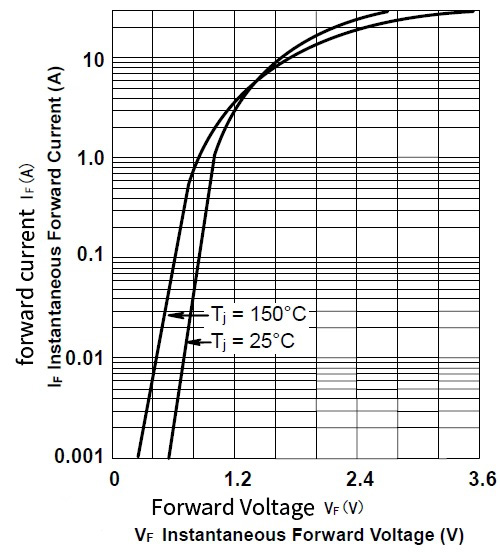
Maximum reverse voltage: The maximum reverse voltage of 1N5408 is 1000V, while the maximum reverse voltage of 1N4007 is 1000V, but the maximum current capacity is lower (1 ampere).
Average rectified current: The 1N5408 has an average rectified current of 3A, while the 1N4007 has an average rectified current of 1A.
Size: 1N5408 is larger than 1N4007.
Price: 1N5408 is more expensive than 1N4007.
1n5408 has lower series resistance and higher conduction efficiency. Therefore, in applications requiring higher power, the 1n5408 may be more suitable.
So how do you choose the right diode?
When choosing a replacement or original design, consider the following:
Maximum Current: Make sure that the selected diode has a maximum current value greater than what is required by the circuit.
Maximum reverse voltage: If the circuit involves reverse voltage, you must ensure that the maximum reverse voltage value of the selected diode is higher than the desired value.
Conduction Efficiency: If performance is important, consider the conduction efficiency of the selected diode.
Package Type: Make sure that the package type of the selected diode is compatible with your circuit.




 Need Help?
Need Help?







